Introduction
In the unpredictable landscape of business, crises can strike without warning, posing significant challenges to organizations. Effective crisis recovery strategies are crucial for businesses to not only survive but emerge stronger from adversity. This article explores key strategies for effective crisis recovery, emphasizing the importance of resilience, adaptability, and strategic decision-making.
Immediate Crisis Assessment
When a crisis occurs, the first step is to assess the situation promptly. Understand the nature and scope of the crisis, identifying potential impacts on stakeholders, operations, and the overall reputation of the business.
Transparent and Timely Communication
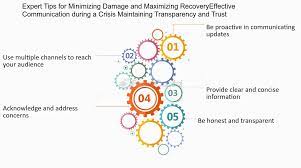
Transparent communication is paramount during a crisis. Keep stakeholders informed about the situation, the actions being taken, and any potential impact on them. Timely updates foster trust and help manage expectations.
Assemble a Cross-Functional Team
Create a crisis management team comprising individuals from different departments, each bringing specific expertise. This team should include representatives from leadership, communications, operations, legal, and human resources.
Clearly Defined Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly define roles and responsibilities within the crisis management team. Establishing a hierarchical structure ensures that decisions can be made swiftly, and tasks are delegated effectively during high-pressure situations.
Agile Decision-Making
In a crisis, conditions can change rapidly. Embrace agile decision-making processes that allow the organization to adapt quickly to evolving circumstances. Flexibility is key to navigating uncertainties with resilience.
Scenario Planning for Future Crises
Learn from the crisis at hand and engage in scenario planning for potential future crises. Anticipate possible challenges, develop response strategies, and implement preventive measures to enhance the organization’s overall preparedness.
Empathy and Understanding
During a crisis, stakeholders may be deeply affected. Demonstrate empathy, understanding, and a genuine commitment to addressing their concerns. Whether it’s customers, employees, or investors, proactive engagement is essential.
Provide Support Systems
Establish support systems for employees and other stakeholders. This may include counseling services, financial assistance, or other resources to help individuals cope with the emotional and practical impacts of the crisis.
Proactive Reputation Management
Actively manage the organization’s reputation by addressing negative narratives and misinformation. Implement communication strategies that highlight the steps taken to resolve the crisis and emphasize the commitment to improvement.
Learning Opportunities
View the crisis as an opportunity to strengthen the organization’s reputation. Demonstrate a commitment to learning from the experience, implementing changes, and continuously improving processes to prevent similar issues in the future.
Financial Assessment and Planning
Conduct a thorough financial assessment to understand the economic impact of the crisis. Develop a financial recovery plan that addresses immediate needs, ensures liquidity, and charts a path towards long-term financial stability.
Explore Funding Options
Consider exploring funding options to inject capital into the business if needed. This may involve engaging with investors, lenders, or government assistance programs that provide financial support during crises.
Adherence to Laws and Regulations
Navigate the crisis while adhering to legal and regulatory requirements. Consult legal counsel to ensure that all actions taken during the recovery process comply with applicable laws, mitigating legal risks and potential liabilities.
Proactive Compliance Measures
Implement proactive measures to enhance compliance in the future. This may involve strengthening internal controls, revising policies and procedures, and investing in training programs to ensure a culture of compliance throughout the organization.
Post-Crisis Evaluation
Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the organization’s response to the crisis. Analyze what worked well, identify areas for improvement, and apply these lessons to enhance future crisis management strategies.
Implement Changes and Enhancements
Based on the post-crisis evaluation, implement necessary changes and enhancements to organizational processes, communication strategies, and crisis response protocols. Continuously seek opportunities for improvement.
Conclusion
Effectively recovering from a crisis requires a strategic and multidimensional approach. By swiftly responding to the crisis, establishing a robust crisis management team, remaining adaptable, and prioritizing stakeholder engagement, organizations can navigate challenges with resilience. Proactive reputation management, financial stabilization, legal compliance, and a commitment to continuous improvement further contribute to successful crisis recovery. Ultimately, viewing a crisis as an opportunity for growth and learning positions organizations to emerge stronger and more resilient than before.