Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic-depressive illness, is a mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings, ranging from manic highs to depressive lows. This disorder can significantly impact a person’s daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. Let’s delve into the symptoms, types, and treatment options for bipolar disorder.
Introduction
Bipolar disorder is a chronic mental health condition marked by alternating periods of mania (elevated mood and energy) and depression (low mood and energy). Understanding the symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment are essential steps in managing this disorder effectively.
Types of Bipolar Disorder
There are several types of bipolar disorder, each characterized by the severity and duration of mood episodes:
Bipolar I Disorder: Involves manic episodes that last for at least seven days or are severe enough to require immediate medical attention. Depressive episodes often accompany these manic phases.
Bipolar II Disorder: Characterized by a pattern of depressive episodes and hypomanic episodes (less severe than full-blown mania). Individuals with Bipolar II may not experience full mania but still face significant mood fluctuations.
Cyclothymic Disorder: Involves chronic mood instability with numerous periods of hypomanic and depressive symptoms lasting for at least two years (one year in children and adolescents).
Manic Episodes
Elevated Mood: Feeling extremely happy, euphoric, or irritable.
Increased Energy: Engaging in hyperactive or impulsive behaviors.
Reduced Need for Sleep: Feeling rested with minimal sleep.
Racing Thoughts: Rapid speech, jumping from topic to topic.
Impaired Judgment: Engaging in risky behaviors without considering consequences.
Depressive Episodes
Sadness or Hopelessness: Persistent low mood or loss of interest in activities.
Fatigue: Persistent feelings of tiredness and low energy.
Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia or excessive sleeping.
Changes in Appetite: Significant weight loss or gain.
Difficulty Concentrating: Impaired focus and decision-making.
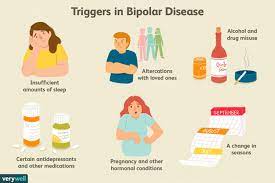
Causes of Bipolar Disorder
The exact cause of bipolar disorder is not fully understood, but a combination of genetic, biological, and environmental factors is believed to contribute. Family history, chemical imbalances in the brain, and stressful life events may all play a role in the development of this disorder.
Medication
Mood Stabilizers: Lithium and certain anticonvulsant medications help stabilize mood and prevent manic or depressive episodes.
Antipsychotics: These medications can be used to manage symptoms during manic episodes.
Antidepressants: Prescribed cautiously, as they can trigger manic episodes in some individuals.
Psychotherapy
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT): Focuses on stabilizing daily routines and managing relationships to regulate mood.
Lifestyle Management
Maintaining Regular Sleep Patterns: Consistent sleep is crucial in managing bipolar disorder.
Avoiding Substance Abuse: Alcohol and drugs can exacerbate symptoms and interfere with medication effectiveness.
Building a Support System: Having a reliable support network can aid in coping with the challenges of bipolar disorder.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
In severe cases or when other treatments are ineffective, ECT may be considered. This involves passing electrical currents through the brain to induce controlled seizures, impacting brain chemistry.
Coping Strategies for Individuals and Families
Education: Understanding the disorder and its symptoms is crucial for individuals and their families.
Open Communication: Encourage open and honest communication about feelings and experiences.
Regular Monitoring: Keeping track of mood changes, triggers, and medication effectiveness.
Seeking Professional Help: Regular therapy sessions and check-ins with mental health professionals are essential components of managing bipolar disorder.
Conclusion
Bipolar disorder is a complex mental health condition that requires a comprehensive and individualized approach to treatment. With the right combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle management, individuals with bipolar disorder can lead fulfilling lives. Seeking support from mental health professionals, building a strong support network, and actively participating in treatment are essential steps toward managing this challenging but manageable disorder.