Introduction
The saying “you are what you eat” takes on a deeper meaning when considering the intricate relationship between nutrition and mental health. Recent research has unveiled the significance of the gut-brain connection, highlighting how the food we consume plays a pivotal role in influencing our mental well-being. In this article, we’ll explore the intricate link between nutrition and mental health, emphasizing the importance of a healthy gut for overall psychological wellness.
The Enteric Nervous System
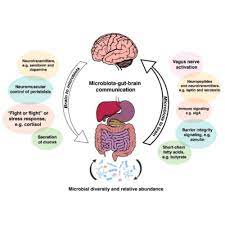
The gut and brain are connected by a complex network of neurons known as the enteric nervous system. This system, sometimes referred to as the “second brain,” communicates bidirectionally with the central nervous system, influencing various aspects of mental health.
Microbiota Influence
The gut is home to trillions of microorganisms collectively known as the microbiota. These microorganisms play a crucial role in maintaining gut health and are increasingly recognized for their impact on mental well-being.
Serotonin Production
Serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation, is largely produced in the gut. Nutrients such as tryptophan, found in protein-rich foods, contribute to serotonin synthesis, influencing mood and emotional well-being.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, abundant in fatty fish and certain nuts and seeds, have been linked to a reduced risk of depression. These essential fats support brain structure and function, impacting mood and cognitive function.
Gut Inflammation and Mental Disorders
An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to inflammation, which has been associated with mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiota is crucial for reducing inflammation and supporting mental well-being.
Gut Permeability and Mental Health
Increased permeability of the gut lining, often referred to as “leaky gut,” may allow harmful substances to enter the bloodstream, potentially affecting the brain and contributing to mental health issues. A balanced diet supports gut integrity.
Probiotics and Fermented Foods
Probiotics, found in fermented foods like yogurt and kimchi, promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria. Regular consumption can positively impact mental health by supporting gut microbiota diversity.
Prebiotic-Rich Foods
Prebiotics, found in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas, serve as fuel for beneficial gut bacteria. Including prebiotic-rich foods in the diet encourages the growth of these beneficial microorganisms.
Whole Foods and Nutrient Diversity
A balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods ensures a diverse range of nutrients. Nutrient diversity supports overall health, including the gut-brain connection, and reduces the risk of nutritional deficiencies linked to mental health issues.
Hydration and Mental Function
Staying hydrated is essential for optimal brain function. Dehydration can negatively impact mood, concentration, and cognitive performance. Adequate water intake supports overall mental well-being.
Physical Activity
Regular exercise has been linked to improved mental health. Physical activity influences gut health and promotes the release of endorphins, contributing to a positive mood.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health and mental well-being. Implementing stress management techniques such as meditation, mindfulness, and adequate sleep supports both the gut-brain connection and overall mental health.
Conclusion
The intricate interplay between nutrition and mental health underscores the importance of cultivating a healthy gut. From influencing neurotransmitter production to impacting inflammation and mood regulation, the gut-brain connection is a dynamic and essential aspect of psychological well-being. By prioritizing a balanced diet, probiotic-rich foods, and lifestyle factors that support gut health, individuals can take proactive steps toward nurturing their mental health from the inside out.