Lung cancer is a formidable adversary, claiming countless lives each year. However, understanding the risk factors, early symptoms, and adopting preventive measures can play a pivotal role in reducing the incidence and impact of this deadly disease. In this article, we delve into the nuances of lung cancer, providing valuable insights into its understanding and prevention.
Introduction
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the lungs, often developing over time due to exposure to carcinogens. It is essential to comprehend the risk factors associated with lung cancer, recognize early signs, and implement preventative strategies to mitigate its prevalence.
Types of Lung Cancer
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC):
Accounting for the majority of lung cancer cases, NSCLC includes subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC):
Although less common, SCLC is known for its aggressive nature and tendency to spread rapidly.
Risk Factors
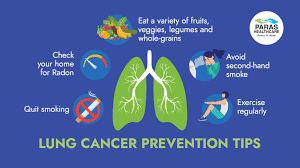
Tobacco Smoke:
Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer. Non-smokers exposed to secondhand smoke are also at risk.
Occupational Exposure:
Exposure to carcinogens like asbestos, radon, and certain chemicals in the workplace can increase the risk of lung cancer.
Family History:
Individuals with a family history of lung cancer may have a higher predisposition to the disease.
Air Pollution:
Prolonged exposure to air pollutants, including outdoor and indoor pollutants, is associated with an increased risk.
Early Symptoms
Persistent Cough:
A persistent or worsening cough, especially if accompanied by blood, should be evaluated.
Breathing Difficulties:
Shortness of breath or wheezing may indicate lung issues, including cancer.
Chest Pain:
Chest pain that is constant or worsens with deep breathing or coughing requires attention.
Unexplained Weight Loss:
Significant and unexplained weight loss can be a symptom of various cancers, including lung cancer.
Prevention Strategies
Smoking Cessation:
Quitting smoking is the most effective way to reduce the risk of lung cancer. Support programs and therapies are available to assist individuals in the quitting process.
Radon Testing:
Radon, a radioactive gas, is a known carcinogen. Testing homes for radon levels and implementing mitigation measures can reduce exposure.
Occupational Safety:
Adhering to safety protocols in workplaces with potential carcinogenic exposures can minimize the risk.
Healthy Lifestyle:
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, contributes to overall well-being and may reduce cancer risk.
Early Detection and Screening
Screening for High-Risk Individuals:
High-risk individuals, such as current or former smokers, may benefit from regular screenings, like low-dose CT scans, to detect lung cancer at an early, more treatable stage.
Awareness of Symptoms:
Being aware of potential symptoms and promptly seeking medical attention can facilitate early diagnosis and intervention.
Treatment Options
Surgery:
Depending on the stage, surgery may involve removing a portion of the lung or the entire lung.
Chemotherapy:
Medications are used to kill cancer cells or slow their growth.
Radiation Therapy:
High-dose radiation is directed at cancer cells to destroy or damage them.
Targeted Therapies:
Targeted drugs aim at specific abnormalities in cancer cells, inhibiting their growth.
Support and Coping
Emotional Support:
A cancer diagnosis can be emotionally challenging. Seeking support from loved ones, support groups, or mental health professionals is crucial.
Lifestyle Adjustment:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including stress management, can enhance the overall quality of life during and after treatment.
Conclusion
Understanding and preventing lung cancer require a multifaceted approach. By recognizing risk factors, being vigilant about symptoms, and implementing lifestyle changes, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their susceptibility. Early detection through screenings and advancements in treatment options further contribute to improving outcomes for those affected by lung cancer.