Living in the digital age has brought about unprecedented convenience, but it has also given rise to sedentary lifestyles that pose significant risks to our health. In this article, we’ll delve into the various aspects of sedentary living, exploring its impact on cardiovascular health, musculoskeletal well-being, and mental health. Additionally, we’ll discuss practical solutions and lifestyle changes to mitigate these health risks.
Introduction
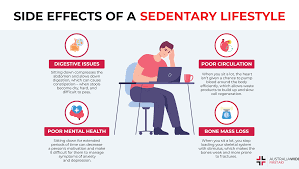
A sedentary lifestyle is characterized by prolonged periods of inactivity and low levels of physical exercise. With the advent of technology and changes in work patterns, more individuals find themselves sitting for extended periods, contributing to a range of health issues. Understanding the consequences of a sedentary lifestyle is crucial for making informed choices about our daily routines.
Health Risks Associated with Sedentary Lifestyles
Cardiovascular Health
Sitting for long periods has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. The lack of movement can lead to elevated blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and a higher likelihood of developing heart-related issues.
Musculoskeletal Issues
Prolonged sitting can take a toll on the musculoskeletal system, leading to issues such as back pain, neck strain, and poor posture. Over time, these problems can become chronic and affect overall mobility.
Mental Health Implications
Sedentary behavior has also been associated with mental health issues, including an increased risk of anxiety and depression. The lack of physical activity can impact neurotransmitter levels and contribute to feelings of lethargy and low mood.
The Role of Physical Activity in Health
Benefits of Regular Exercise
Incorporating regular physical activity into daily life is essential for maintaining overall health. Exercise helps improve cardiovascular fitness, strengthen muscles and bones, and support mental well-being by releasing endorphins.
Guidelines for Physical Activity
Health experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. This can include activities like brisk walking, cycling, or engaging in sports. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises at least twice a week is beneficial for overall health.
Workplace Challenges and Solutions
Sedentary Jobs and Health Impact
Many modern jobs require long hours of sitting, contributing to the sedentary epidemic. Recognizing the health impact of sedentary jobs is the first step in addressing this issue.
Incorporating Movement into Workdays
Implementing strategies such as standing desks, taking short breaks to stretch, and encouraging walking meetings can help counteract the negative effects of sedentary work environments.
Technological Influences
Screen Time and Its Effects
The rise of technology has led to increased screen time, affecting both adults and children. Excessive screen time is associated with sedentary behavior and can contribute to various health issues.
Digital Detox Strategies
Setting limits on screen time, taking breaks to stretch or walk, and creating tech-free zones in the home can help reduce the impact of excessive screen time on health.
Sedentary Behavior in Children and Adolescents
Long-Term Health Consequences
Children and adolescents are also susceptible to the effects of sedentary living, which can have long-term consequences for their health and development.
Encouraging Active Lifestyles from a Young Age
Promoting physical activity in schools, limiting screen time for children, and encouraging outdoor play are crucial for establishing healthy habits early in life.
Social and Environmental Factors
Urbanization and Sedentary Living
Urban environments often contribute to sedentary living, with limited green spaces and increased reliance on transportation. Addressing these environmental factors is essential for promoting active lifestyles.
Social Influences on Lifestyle Choices
Social norms and peer influences play a significant role in shaping lifestyle choices. Creating a culture that values and prioritizes physical activity can positively impact individual behaviors.
Creating an Active Lifestyle
Small Changes for Big Impact
Incorporating small changes into daily routines, such as taking the stairs, walking instead of driving short distances, or participating in active hobbies, can have a significant impact on overall health.
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting achievable and realistic goals for physical activity helps individuals stay motivated and gradually build healthier habits.
Education and Awareness
Promoting Health Literacy
Raising awareness about the health risks of sedentary behavior and promoting health literacy empowers individuals to make informed choices about their lifestyles.
Public Health Campaigns
Government and public health initiatives can play a crucial role in promoting physical activity through campaigns, policies, and community programs.
The Importance of Ergonomics
Proper Posture and Its Impact
Maintaining good posture is essential, especially for those with sedentary jobs. Ergonomic furniture and workspace setups can support proper posture and reduce the risk of musculoskeletal issues.
Ergonomic Solutions for Sedentary Activities
Incorporating ergonomic solutions, such as standing desks, ergonomic chairs, and regular breaks for stretching, can enhance comfort and reduce the negative impact of sedentary activities.
Balancing Screen Time and Physical Activity
Establishing Healthy Habits
Creating a balance between screen time and physical activity is crucial for overall health. Establishing routines that include dedicated time for exercise and leisure away from screens promotes a healthier lifestyle.
Finding a Balance in the Digital Age
Recognizing the need for a balanced approach to technology use helps individuals maintain a healthy relationship with screens while prioritizing their physical well-being.
Health Benefits of Standing Desks
Reducing Sedentary Time at Work
Standing desks offer a practical solution to reduce sitting time at work, promoting better posture and increased movement throughout the day.
Incorporating Standing Breaks
Encouraging short standing breaks during work hours further reduces the negative impact of prolonged sitting and contributes to a more active work environment.
Community Initiatives and Programs
Creating Active Spaces
Communities can benefit from initiatives that create active spaces, such as parks, walking trails, and bike paths. Accessible recreational areas promote physical activity for individuals of all ages.
Incentivizing Physical Activity
Implementing incentives, such as community events, rewards programs, and fitness challenges, encourages individuals to engage in regular physical activity.
Motivation and Overcoming Barriers
Identifying and Addressing Obstacles
Understanding personal barriers to physical activity and finding practical solutions helps individuals overcome challenges and stay committed to an active lifestyle.
Finding Personal Motivation
Discovering intrinsic motivation, whether it’s the desire for improved health, increased energy, or enhanced well-being, plays a crucial role in sustaining long-term lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
The impact of sedentary lifestyles on health is profound, affecting various aspects of physical and mental well-being. Recognizing the risks associated with prolonged inactivity is the first step in making positive lifestyle changes. By incorporating regular physical activity, addressing workplace challenges, and promoting awareness, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the negative effects of sedentary living.